Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept confined to science fiction. It’s here, powering the apps you use, the cars you drive, and even the recommendations you see while shopping online. From self-learning systems to intelligent chatbots, AI has quietly become the digital backbone of our connected world.
In this detailed article, we’ll explore what artificial intelligence truly means, how it works, its branches, applications across industries, major benefits, challenges, and what the future may hold. Whether you’re a student, professional, or business leader, understanding AI is critical to navigating the technological landscape of the 21st century.
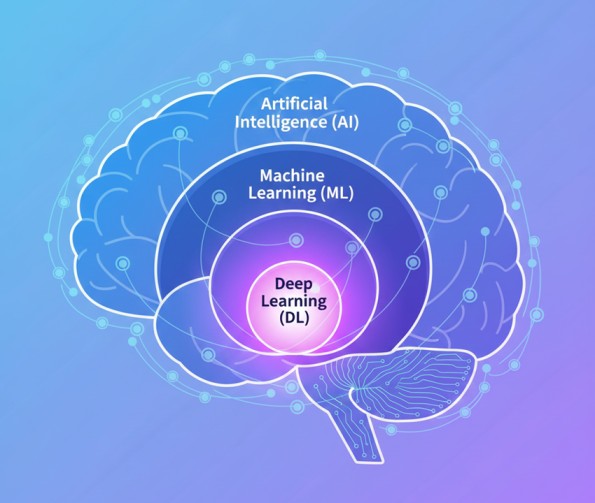
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
At its core, Artificial Intelligence refers to the ability of a computer or machine to mimic human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. The idea is to enable machines to “think” and act intelligently — much like humans, but often faster and more accurately.
In simple terms, AI allows computers to perform tasks that once required human intelligence. These can include:
- Recognizing speech or images
- Understanding natural language
- Making predictions or recommendations
- Playing games strategically
- Driving vehicles autonomously
The concept of AI was first popularized in the 1950s, when pioneering scientists like Alan Turing, John McCarthy, and Marvin Minsky began exploring whether machines could simulate human intelligence. John McCarthy, in particular, coined the term Artificial Intelligence in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, which marked the beginning of AI as a field of research.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
AI works through the combination of data, algorithms, and computational power. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
- Data Collection:
AI systems start with data — massive volumes of text, audio, video, images, and numbers. The more data available, the better the system can learn patterns. - Data Processing:
Raw data is cleaned, structured, and labeled for training. For instance, in image recognition, pictures are tagged with labels like “cat” or “dog”. - Model Training:
The AI system uses algorithms (sets of mathematical instructions) to learn patterns in this data. This is often achieved through machine learning (ML), where models improve their performance automatically as they are exposed to more data. - Prediction and Decision Making:
Once trained, the model can make predictions — for example, forecasting stock prices, recognizing faces, or diagnosing diseases. - Feedback and Optimization:
AI systems refine themselves over time. They test predictions, receive feedback, and adjust their algorithms for better accuracy. This self-improvement capability is what differentiates AI from traditional software.
Modern AI systems heavily rely on neural networks — mathematical models inspired by the human brain’s structure. These networks enable deep learning, a subset of machine learning that processes vast amounts of unstructured data (like images, text, and sounds) to perform complex tasks with remarkable precision.
The Core Branches of Artificial Intelligence
AI isn’t a single technology but an umbrella term covering multiple specialized areas. Let’s explore the major branches:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the backbone of modern AI. It enables machines to learn from data patterns and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming.
Key types of machine learning include:
- Supervised Learning: Models are trained on labeled data. Example: email spam detection.
- Unsupervised Learning: Models find patterns in unlabeled data. Example: customer segmentation.
- Reinforcement Learning: Models learn through trial and error, receiving rewards for correct actions. Example: AI in gaming and robotics.
Read More: What Is Machine Learning?
2. Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to process complex data. It is especially effective in image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and autonomous driving.
For instance, deep learning powers systems like Google Photos, Siri, and ChatGPT, enabling them to understand speech, visuals, or written text at a human-like level of intelligence.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It’s what allows chatbots, voice assistants, and machine translators to function.
Applications include:
- Sentiment analysis
- Language translation
- Text summarization
- Question-answering systems
4. Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world — such as images and videos. This technology powers facial recognition systems, autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and more.
5. Robotics
Robotics combines AI and physical machinery to create intelligent robots capable of performing complex tasks. From automated manufacturing robots to delivery drones and surgical robots, the integration of AI has taken robotics to a new level.
6. Expert Systems
Expert systems are AI programs designed to emulate the decision-making skills of human experts. They use rule-based reasoning and are commonly applied in domains like finance, medicine, and engineering for diagnostic or advisory functions.
Real-World Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI has transformed nearly every industry. Here’s a look at some of the most influential applications:
1. Healthcare
AI assists doctors in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and predicting patient outcomes. Tools like IBM Watson Health use AI to recommend treatments based on patient data.
2. Finance
In banking and finance, AI detects fraud, automates trading, personalizes customer experiences, and assesses credit risks. Robo-advisors like Betterment use AI to manage investments intelligently.
3. Retail and E-commerce
AI drives recommendation engines on platforms like Amazon and Netflix by analyzing user behavior to predict preferences. It also optimizes pricing, supply chain management, and inventory control.
4. Education
AI-based tools personalize learning experiences, automate grading, and provide intelligent tutoring. Platforms like Coursera or Duolingo use AI to adapt to each learner’s skill level.
5. Transportation
Self-driving cars, route optimization, and predictive maintenance are made possible through AI. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber rely on deep learning to make their vehicles navigate safely.
6. Marketing
AI analyzes customer data to optimize campaigns, personalize outreach, and improve conversion rates. Predictive analytics helps marketers identify trends before they happen.
7. Manufacturing
Smart factories use AI-powered robots and sensors to streamline production, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
AI brings a wealth of advantages, reshaping industries and societies:
- Efficiency and Automation: AI takes over repetitive or dangerous tasks, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Machine algorithms can process massive data volumes without fatigue or errors.
- Personalization: From online shopping to entertainment, AI personalizes user experiences.
- Predictive Insights: Businesses can forecast demand, customer churn, or market trends.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights make business and healthcare decisions more reliable.
Challenges and Risks of Artificial Intelligence
While AI is incredibly powerful, it’s not without its challenges:
- Bias in Data: If AI systems are trained on biased data, they can produce unfair or discriminatory results.
- Job Displacement: Automation may replace certain human roles, leading to workforce disruptions.
- Privacy Concerns: AI often requires large datasets, raising questions about data protection and consent.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake — the developer, the user, or the machine itself?
- Cost and Complexity: Building and maintaining AI systems is expensive and requires specialized expertise.
Addressing these challenges requires transparent algorithms, ethical standards, and global cooperation to ensure responsible AI development.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI is both exciting and uncertain. Experts predict that the next decade will witness advancements such as:
- Explainable AI (XAI): Making algorithms more transparent and understandable.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Machines with human-like reasoning abilities capable of complex problem-solving.
- AI in Climate Change: Using machine learning to model environmental impacts and improve sustainability.
- Neurosymbolic AI: Combining deep learning with logic-based reasoning for more robust understanding.
- Quantum AI: Leveraging quantum computing to exponentially increase AI processing capabilities.
Governments and organizations are also focusing on AI governance frameworks to ensure that innovation doesn’t come at the cost of ethics or human values.
Artificial Intelligence vs. Human Intelligence
While AI can perform certain tasks faster and more precisely, it still lacks true consciousness and emotional understanding. Human intelligence is flexible, creative, and empathetic — qualities that machines haven’t mastered yet.
AI, in contrast, excels at specific, narrow tasks (known as narrow AI) such as chess playing or speech recognition. The ultimate goal — Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) — aims to create machines that can reason, plan, and learn across any domain like a human being.
However, achieving AGI remains one of the biggest scientific challenges of our time.
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence represents a paradigm shift in how humans interact with technology. It is reshaping industries, driving innovation, and unlocking possibilities that once seemed impossible. However, it also comes with enormous responsibility — to use its power ethically and equitably.
As a senior data scientist, I’ve seen firsthand how AI can empower businesses and individuals. Understanding its fundamentals isn’t just a technical necessity — it’s a societal one. The more we demystify AI, the better we can harness it to create a smarter, fairer, and more sustainable world.
FAQs on Artificial Intelligence
Why is AI important today?
AI helps automate work, improve accuracy, speed up decision-making, and reduce human effort. It powers tools we use daily—like chatbots, voice assistants, YouTube recommendations, online shopping suggestions, and modern productivity apps.
How is Machine Learning related to AI?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI.
AI is the broad field; ML focuses on teaching machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML helps AI systems improve over time.
What is Deep Learning, and how is it different from Machine Learning?
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of Machine Learning.
It uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns automatically.
While ML needs some human feature selection, DL learns everything from raw data—images, audio, text, etc.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of AI that creates new content such as text, images, videos, music, and code.
Examples include ChatGPT, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and Claude.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are systems that can think, decide, and take actions on behalf of a user.
They can perform tasks like research, scheduling, automation, customer support, or data processing with minimal human involvement.
Can AI fully replace humans?
AI can automate repetitive tasks but cannot replace human creativity, emotional understanding, ethical judgment, or strategic decision-making.
AI is best used as a helper, not a replacement
How does AI learn?
AI learns by analyzing large amounts of data, recognizing patterns, and adjusting its internal rules (parameters) to improve accuracy over time.
The more data it gets, the better it becomes.